Titanic- Machine Learning Disaster
This a challenge on Kaggle where we are given a dataset of the passengers on the titanic ship and we need to build a model that predicts the people who survived.
There are two datasets test.csv and train.csv. In train data there is a column named "Survived" which is the target column for us. We need to use test dataset to predict the results.
1. The first step is loading data.
Code:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount("/content/drive")
train_data=pd.read_csv("/content/drive/My Drive/Dataset/train.csv")
train_data.head()
test_data=pd.read_csv("/content/drive/My Drive/Dataset/test.csv")
test_data.head()
2.The next step is data cleaning. We will see if any null values are present in the data
Code:
train_data.isnull().sum()
Output:
PassengerId 0 Survived 0 Pclass 0 Name 0 Sex 0 Age 177 SibSp 0 Parch 0 Ticket 0 Fare 0 Cabin 687 Embarked 2 dtype: int64
Code:
test_data.isnull().sum()
Output:
PassengerId 0 Pclass 0 Name 0 Sex 0 Age 86 SibSp 0 Parch 0 Ticket 0 Fare 1 Cabin 327 Embarked 0 dtype: int64
There are 177 null values in Age column of train data and 86 null values in Age column of test data. Now we fill the null values with the mean value of the age.
Code:
train_data['Age']=train_data['Age'].fillna(train_data['Age'].mean())
train_data['Age'].isnull().sum()
test_data['Age']=test_data['Age'].fillna(test_data['Age'].mean())
test_data['Age'].isnull().sum()
Output:
0 0
3. In the data Age and Fare are not categorical values. We need to convert them to categorical values. We can use cut method in pandas library to divide the values into intervals.
Code:
train_data['agegroup']=pd.cut(train_data.Age, bins=[0.0,3.0, 16.0, 40.0,60.0,80.1], right=False, labels=[1, 2, 3,4,5])
test_data['agegroup']=pd.cut(test_data.Age, bins=[0.0,3.0, 16.0, 40.0,60.0,80.1], right=False, labels=[1, 2, 3,4,5])
A new column named agegroup is added to the data. In contains the labels to which a passenger age belongs to. We add this column to both train data and test data.
train_data['faregroup']=pd.cut(train_data.Fare, bins=[0,100.0,200.0,300.0,512.4000], labels=[ 1,2,3,4])
test_data['faregroup']=pd.cut(test_data.Fare, bins=[0,100.0,200.0,300.0,512.4000], labels=[ 1,2,3,4])
A new column named faregroup is added to the data. In contains the labels to which a passenger fare belongs to. We add this column to both train data and test data.
4. There are many columns in the data but all are not useful for us. We use only some of the columns.
The selected columns are: "Pclass", "Sex","agegroup","faregroup","Embarked","SibSp", "Parch"
5. The next step is model building. I used Random Forest Classifier. I used train data for training the model and test data to predict the results.
Code:
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from google.colab import files
y = train_data["Survived"]
features = ["Pclass", "Sex","agegroup","faregroup" ,"Embarked","SibSp", "Parch"]
X = pd.get_dummies(train_data[features])
X_test = pd.get_dummies(test_data[features])
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, max_depth=5, random_state=1)
model.fit(X, y)
predictions = model.predict(X_test)
output = pd.DataFrame({'PassengerId': test_data.PassengerId, 'Survived': predictions})
output.to_csv('submission.csv', encoding = 'utf-8-sig')
files.download('submission.csv')
print("Your submission was successfully saved!")
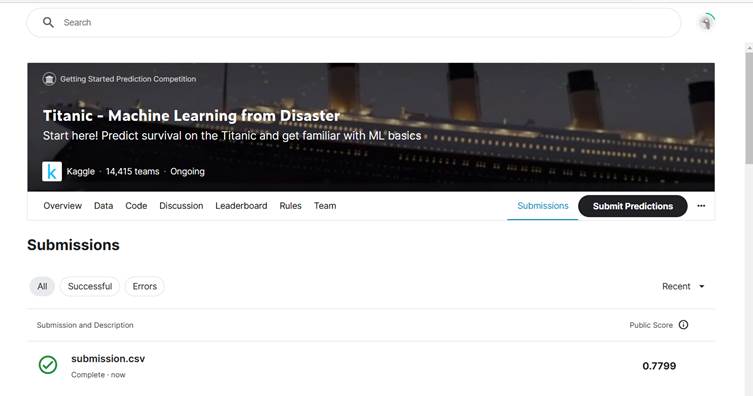
After submitting the generated csv file in Kaggle website, I got a final score of 0.7799 which is slightly higher than the original 0.77511
The final output is
References:
1 Ways to import CSV files in Google Colab - GeeksforGeeksUsed code from here to import a file in google colab
2 Pandas Cut - Continuous to Categorical - GeeksforGeeks Used the syntax of cut method from here. The bins and labels are according to the data.
3 Titanic Tutorial | Kaggle Used the Random Forest Classifier syntax from here.
4 Google Colab: 3 Ways To Save Pandas Dataframe Data (cyublog.com) Used code from here to download a csv file in google colab.
Contribution:
1 Identified that there are many null values in Age column and filled the null values with mean value of that column.
2 Converted Age column and Fare column into categorical values by defining the bins and labels.