Text
Classification using Naive Bayes Classifier
The main objective of this assignment is
classification of a review into fresh or rotten by applying naive bayes
classifier on the given dataset. Now, we will discuss about Naive Bayes
Classifier
Naive Bayes Classifier: It is based on Bayes theorem which is as follows.
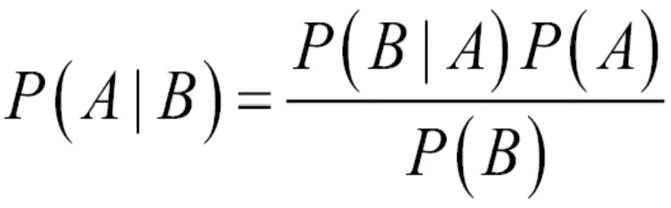
In the above formula P(A|B) is conditional
probability. We will discuss more about how to use classifier by using an
example from the data set.
Data Set: We have the rotten tomato review data set. There are
480000 rows and 2 columns. The columns are "Freshness" and "Review". In the "Freshness"
column there are reviews and, in the column "Review" there are only two values
fresh and rotten depending on the review. The data set is as follows.

Now let us see how to use Naive Bayes
Classifier on a review. Let us consider there is a review "Long, unfocused film".
Our task is to classify this as rotten or fresh. Let us use Bayes theorem formula.
We have to find P (fresh/ "Long, unfocused
film") and P(rotten/ "Long, unfocused film"). Whichever
probability is higher that will be the class of the sentence.
We will see mathematical approach.

CODE:
1. The first step is to divide the data set into train, test, and
development. I decided to split into 60% train, 20% test and 20% development.
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
train_size=0.6
train,rem = train_test_split(df, train_size=0.6)
test_size = 0.5
dev,test = train_test_split(rem,
test_size=0.5)
2.
Next,
I stored all the reviews of the train data in a list
col_list = train['Review'].tolist()
3. Now, I
store all the words of the above list and their corresponding frequency (number
of documents containing the word) in a dictionary.
import re
word_count = {}
for row in col_list:
words = list(set(re.split("[!. _,@?:-=
]", row.lower())))
words = [i for i in words if i !='']
for word in words:
if word in word_count:
word_count[word]
+= 1
else:
word_count[word]
= 1
4.
Now, I stored all reviews in the train data which are fresh in one
list and the reviews which are rotten in another list.
freshData = []
rottenData = []
for i,
row in train.iterrows():
if row['Freshness'] == "fresh":
freshData.append(row['Review'])
if row['Freshness'] == "rotten":
rottenData.append(row['Review'])
freshData = [x.lower() for x in freshData]
rottenData = [x.lower() for x in rottenData]
5.
In the next step I stored all the words in fresh list and their
frequency in a dictionary and all the words in rotten list and their frequency
in another dictionary
import re
fresh_count = {}
for row in freshData:
words = list(set(re.split("[!. _,@?:-=]",
row.lower())))
words = [i for i in words if i !='']
for word in words:
if word in fresh_count:
fresh_count[word]
+= 1
else:
fresh_count[word]
= 1
rotten_count = {}
for row in rottenData:
words = list(set(re.split("[!. _,@?:-=]",
row.lower())))
words = [i for i in words if i !='']
for word in words:
if word in rotten_count:
rotten_count[word]
+= 1
else:
rotten_count[word]
= 1
6.
Now, I counted total rows in train data, number of rows which are
fresh and number of rows which are rotten.
total_count=train['Review'].count()
count_rotten=len(rottenData)
count_fresh=len(freshData)
7.
Now, I found the probability of fresh and probability of rotten.
prob_rotten=count_rotten/total_count
prob_fresh=count_fresh/total_count
print(prob_rotten,prob_fresh)
8. Now, I
defined a function to predict the class of a review passed as a parameter using
the Bayes theorem formula which I mentioned above.
def predict_class(review):
a=re.split("[!.
_,@?:-= ]",review.lower())
a = [i for i in a if i !='']
ans_rotten=1
ans_fresh=1
for ele in a:
ans_rotten=ans_rotten*rotten_count.get(ele, 0)/count_rotten
ans_fresh=ans_fresh*fresh_count.get(ele, 0)/count_fresh
fresh_prob=(ans_fresh*prob_fresh)/(ans_fresh*prob_fresh+
ans_rotten*prob_rotten)
rotten_prob=(ans_rotten*prob_rotten)/(ans_fresh*prob_fresh+
ans_rotten*prob_rotten)
if(fresh_prob>rotten_prob):
return "fresh"
else:
return "rotten"
9.
Now I iterated through the entire development data and run the above
the function for each review and stored the result in a new list
pred=[]
for i,row in dev.iterrows():
pred.append(predict_class(row['Review']))
10.
Now, I calculated the accuracy.
total=len(pred)
count=0
for i
in range(total):
if pred[i]==d[i]:
count=count+1
accuracy = count/total
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy:.2f}")
11.
I got the accuracy as 0.76. Now I applied the concept of smoothing.
The formula is.

12.
I tried using various alpha values like 1, 100,0.01, and 0.1 and
got the accuracies 0.81, 0.77, 0.80 and 0.81. I got the best accuracy for alpha
values 1 and 0.1. The update code after smoothing is
def predict_class_smooth_newer(review):
a=re.split("[!.
_,@?:-= ]",review.lower())
a = [i for i in a if i !='']
ans_rotten=1
ans_fresh=1
for ele in a:
if(ele in rotten_count):
ans_rotten*=(rotten_count[ele]+0.1)/(count_rotten+0.1*2)
if(ele not in rotten_count):
ans_rotten*=(0.1)/(count_rotten+0.1*2)
if(ele in fresh_count):
ans_fresh*=(fresh_count[ele]+0.1)/(count_fresh+0.1*2)
if(ele not in fresh_count):
ans_fresh*=(0.1)/(count_fresh+0.1*2)
fresh_prob=(ans_fresh*prob_fresh)/(ans_fresh*prob_fresh+
ans_rotten*prob_rotten)
rotten_prob=(ans_rotten*prob_rotten)/(ans_fresh*prob_fresh+
ans_rotten*prob_rotten)
if(fresh_prob>rotten_prob):
return "fresh"
else:
return "rotten"
13.
Next, I found top ten words in each class fresh and rotten.
import operator
sorted_d = dict( sorted(fresh_count.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1),reverse=True))
print('Dictionary in descending order
by value : ',sorted_d)
first_ten = list(sorted_d.items())[:10]
print(first_ten)
import operator
sorted_r = dict( sorted(rotten_count.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1),reverse=True))
print('Dictionary in descending order
by value : ',sorted_r)
first_ten = list(sorted_r.items())[:10]
print(first_ten)
14. The
top ten words in fresh class are:
[('the',
91524), ('a', 81869), ('and', 78512), ('of', 70965),
('is', 50864), ('to', 49819), ('in', 40605), ('that', 33157), ('it', 30177),
('with', 26787)]
15. The
top ten words in rotten class are:
[('the', 91578), ('a', 74986), ('of', 64886), ('and', 64094), ('to', 55938), ('is', 45947), ('in', 37449), ('that', 33169), ('it', 31956), ('but', 28438)] 16. The top ten words in each class are stop words. Now we try removing them.
stop_words=['ourselves',"it's",..]
for key in stop_words: del sorted_d[key]first_ten = list(sorted_d.items())[:10]
print(first_ten) for key in stop_words: del sorted_r[key]first_ten = list(sorted_r.items())[:10]
print(first_ten) 17. Now the top ten words in fresh class are:
[('film', 22423), ('movie', 14005), ('one', 11568), ('like', 8305), ('story', 8014), ('best', 5630), ('even', 5602), ('good', 5476), ('much', 4869), ('time', 4665)] 18. Now the top ten words in rotten class are:
[('film', 18477), ('movie', 18246), ('like', 11857), ('one', 9650), ('much', 7923), ('story', 7102), ('even', 6455), ("doesn't", 5308), ('good', 5063), ('make', 4978)]19. Now I applied the hyperparameters of alpha 1 and 0.1 on test data.
When alpha is 1 the accuracy is 0.81 When alpha is 0.1 the accuracy is 0.81 Contribution:
1. I segregated all the reviews based on freshness, calculated frequency of each word and stored in two separate dictionaries.
2. I have written a function which classifies the given review by applying Bayes theorem formula.
3. I calculated the accuracy of development data set and test dataset.
4. I applied the concept of smoothing by taking various alpha values.
5. I removed stop words from the dictionaries to calculate top ten words in each class.
Technical Challenges and solution:1. Initially it became very difficult for me to divide a sentence into words using multiple delimiters. Then I used regular expressions which made my job easy.
2. When I first run the function to classify reviews, I got an error which could not handle divide by zero. Despite of getting error, the execution was successful, and I was able to calculate accuracy.
Then I used concept of smoothing to remove zero probabilities.3. When I tried to calculate top ten words in each class, the result was all common words. Then I removed all those words from the dictionary and again calculated top 10 words.
References:
1] How
to split data into three sets (train, validation, and test) And why? | by
Samarth Agrawal | Towards Data Science. In step 1, I used the code from this
link to divide the dataset into three parts.
2] Python
Regular Expression Tutorial with RE Library Examples | DataCamp.
In step 3, I used the code from this link to write regular expression for
splitting a string.
3] Laplace
smoothing in Naive Bayes algorithm | by Vaibhav Jayaswal | Towards Data Science.
In step 11, I used the concept of Laplace smoothing from this link.
4] Python:
Sort (ascending and descending) a dictionary by value - w3resource. In step
13, I used the code from this link to sort the dictionary.
5] Removing
stop words with NLTK in Python - GeeksforGeeks. In
step 16, I used the stop words from this link.